Introduction
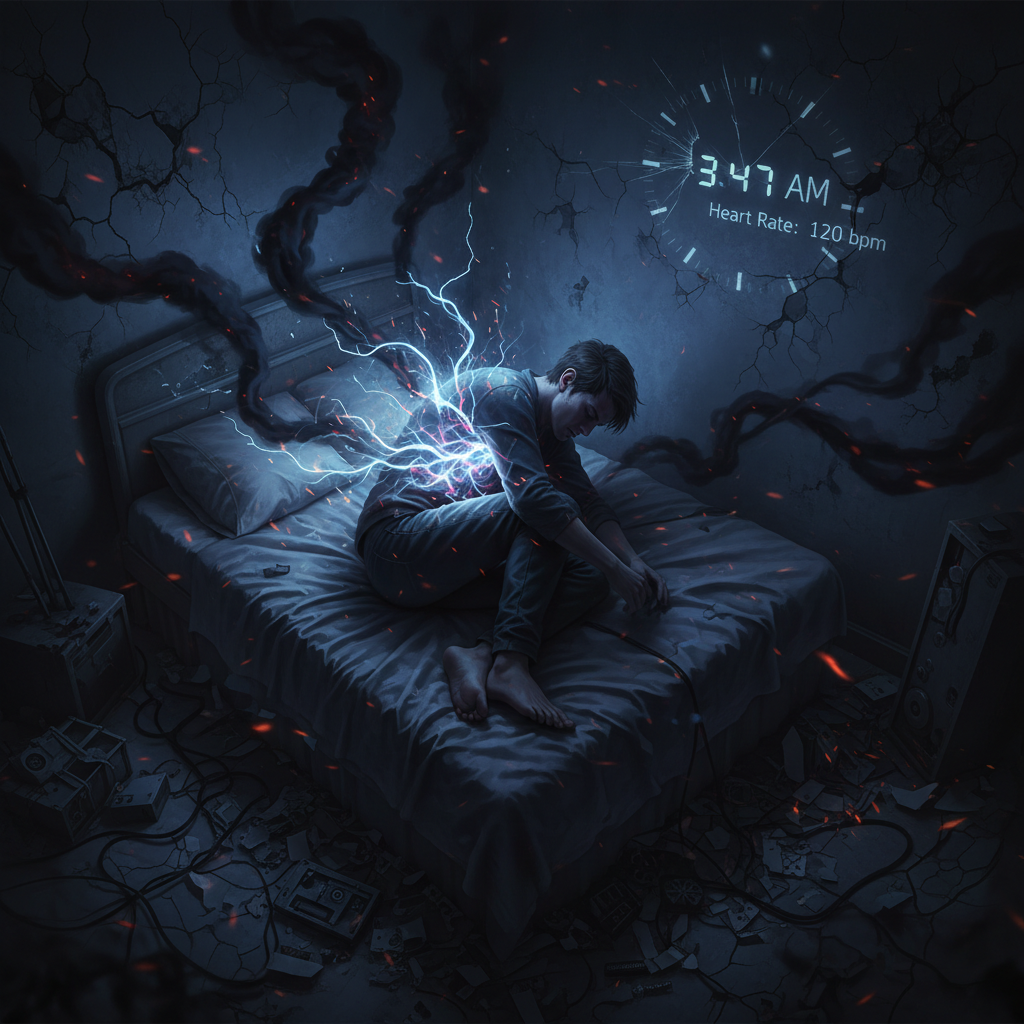
In the modern age of fitness and health, pushing one’s limits has become a common mantra for athletes and gym enthusiasts alike. However, many overlook the grave consequences of overtraining, a condition that occurs when the body is subjected to excessive physical stress without adequate rest and recovery. While dedicated training regimens can elevate performance, overtraining can lead to a significant decline in physical and mental well-being, particularly affecting sleep cycles.
Understanding Overtraining
When individuals overtrain, the body experiences elevated cortisol levels, a hormone associated with stress. High cortisol levels can lead to disturbances in the body’s circadian rhythm, fundamentally altering the way one sleeps. Furthermore, the physical strain can cause discomfort and pain, making it increasingly difficult to fall and stay asleep. Therefore, understanding the relationship between overtraining and sleep is essential for anyone pursuing fitness goals.
The Physiological Effects of Overtraining on Sleep
Additionally, overtraining can disrupt the production of melatonin, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep-wake cycles. When the body is under constant stress, melatonin levels may drop, making it challenging to achieve deep, restorative sleep. As a result, individuals may experience insomnia or restless sleep, further exacerbating feelings of fatigue and reducing overall performance.
Looking for the best option related to Overtraining Sleep Cycles?
The Sleep Bridge recommends checking the latest deals and reviews before purchasing to ensure better sleep quality.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Overtraining
Other symptoms associated with OTS can include mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and lack of motivation. These mental and emotional changes may lead to a cycle of overtraining, as individuals may respond with even more training in an attempt to overcome perceived shortcomings. It is vital for athletes and fitness enthusiasts to tune into their bodies and recognize these signs in order to take preventive measures before overtraining spirals out of control.
The Impact of Poor Sleep on Performance
Studies have shown that athletes who experience regular poor sleep quality may see a reduction in muscle recovery and an increase in exercise-induced inflammation. Additionally, sleep deprivation can raise the likelihood of mental fatigue, ultimately impacting motivation and training consistency. Therefore, prioritizing quality sleep is crucial for athletes to maintain peak performance while reducing the risk of overtraining.
Strategies for Recovery and Improved Sleep
Nutrition also plays a pivotal role in recovery. A balanced diet rich in proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates can provide the necessary nutrients to support recovery and promote good sleep hygiene. Additionally, incorporating supplements like magnesium or omega-3 fatty acids may help regulate sleep patterns and reduce muscle soreness.
Creating an optimal sleep environment can further enhance recovery. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, minimizing exposure to screens before bedtime, and creating a comfortable sleeping environment. Prioritizing mindfulness practices, such as meditation or deep-breathing exercises, can also reduce stress and promote relaxation, ensuring a more restful night’s sleep.
Conclusion
The dangers of overtraining extend far beyond physical fatigue; they significantly affect sleep cycles and overall well-being. By understanding the physiological impact of overtraining, recognizing the associated symptoms, and implementing effective recovery strategies, individuals can prevent the downward spiral of impaired sleep and performance. Prioritizing both training and recovery is essential for anyone looking to achieve their fitness goals sustainably.
Ultimately, fostering a balanced approach to training will not only improve performance but also protect mental health and encourage long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes overtraining syndrome?
+
Overtraining syndrome is caused by excessive physical stress without adequate rest, leading to hormonal imbalances and fatigue.
Can overtraining affect my mental health?
+
Yes, overtraining can lead to mood swings, irritability, and anxiety, significantly impacting mental health and overall well-being.
What role does nutrition play in recovery from overtraining?
+
Nutrition is vital for recovery; a balanced diet supports muscle repair and overall health, promoting better sleep and recovery outcomes.