Introduction
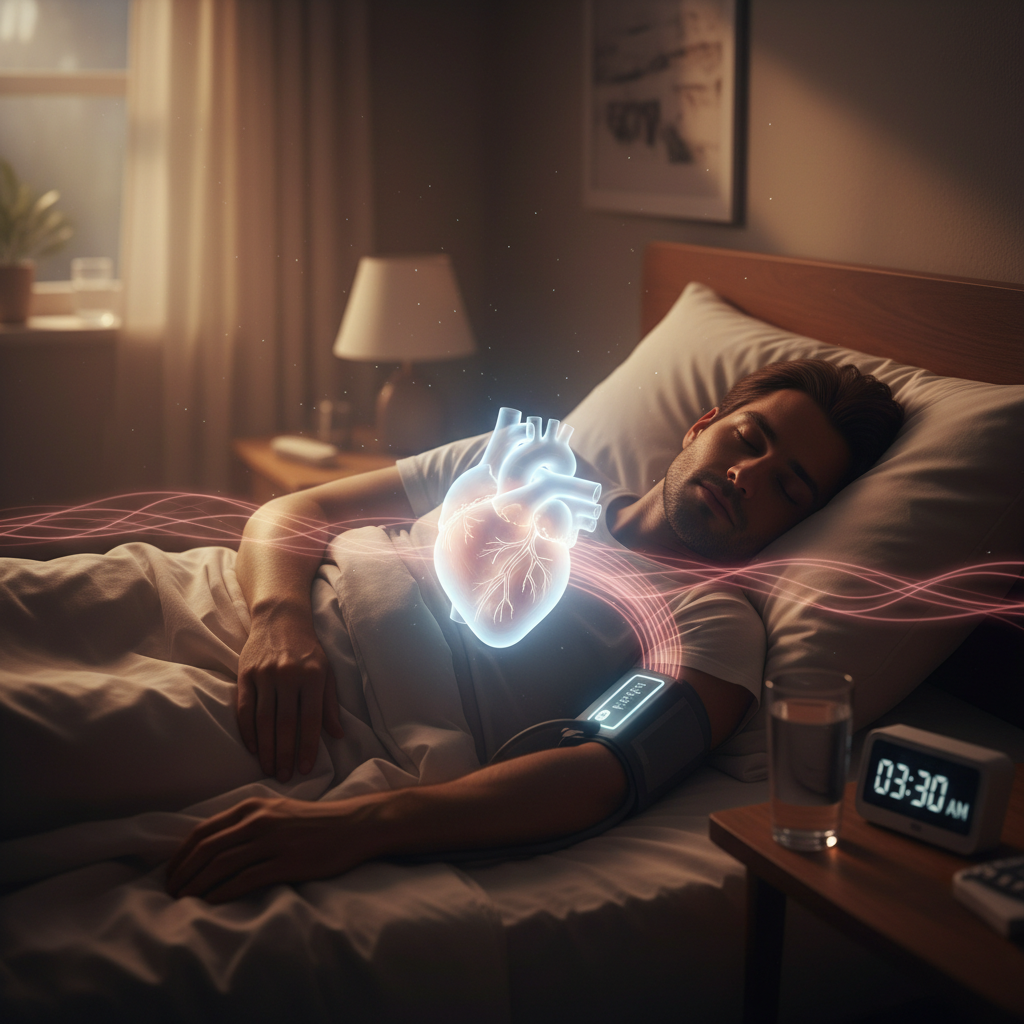
In today’s fast-paced world, sleep often takes a backseat to our daily responsibilities and commitments. Yet, the importance of a good night’s rest cannot be overstated—especially when it comes to cardiovascular health. A growing body of research suggests that there is a significant link between sleep and blood pressure, making it essential for individuals to prioritize quality sleep for optimal heart health.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore how sleep affects blood pressure, the mechanisms behind this relationship, and practical steps you can take to ensure you get the restorative rest you need.
The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Blood Pressure
Moreover, sleep deprivation can affect important health metrics, such as glucose metabolism and overall cardiovascular function. As sleep becomes inadequate, your body may struggle to effectively regulate blood pressure, setting the stage for long-term health challenges. Therefore, prioritizing a consistent sleep routine can play an essential role in managing blood pressure effectively.
The Role of Sleep Disorders
Additionally, insomnia can lead to an array of issues, including elevated stress levels, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating, further exacerbating blood pressure problems. Individuals who struggle with sleep issues should consult healthcare professionals for appropriate diagnosis and treatment, as addressing these disorders can improve both sleep quality and blood pressure levels.
Looking for the best option related to Sleep and Blood Pressure Link?
The Sleep Bridge recommends checking the latest deals and reviews before purchasing to ensure better sleep quality.
Exploring the Sleep-Blood Pressure Relationship
Moreover, the quality of sleep matters just as much as the quantity. Fragmented or poor-quality sleep can lead to suboptimal health outcomes, including the disruption of normal daily circadian rhythms, which influences the regulation of blood pressure. High-quality sleep involves reaching all stages of the sleep cycle, especially the restorative phase of deep sleep. Focusing on both sleep duration and quality can yield beneficial effects for maintaining healthy blood pressure.
The Benefits of Good Sleep Hygiene
1. Maintain a consistent sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body’s internal clock.
2. Create a conducive sleep environment: Keep your bedroom cool, quiet, and dark to promote better sleep.
3. Limit screen time before bed: Exposure to blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with melatonin production and disrupt sleep.
4. Incorporate relaxation techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or gentle stretching can help lower stress and prepare the mind for sleep.
By implementing these strategies, individuals not only enhance their sleep quality but can also contribute significantly to maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Making Lifestyle Changes to Protect Your Heart
Combining these lifestyle changes creates a holistic approach to cardiovascular health. As you address sleep quality, you will likely notice improvements in overall well-being, mood, and energy levels, ultimately contributing to better management of blood pressure and a reduced risk of chronic conditions.
Conclusion
The link between sleep and blood pressure is undeniable. As research continues to affirm the critical role of quality sleep in maintaining cardiovascular health, we must prioritize healthy sleep habits as part of a comprehensive approach to well-being. By understanding how sleep deprivation, sleep disorders, and good sleep hygiene practices can impact blood pressure, individuals can take proactive steps toward improving not only their sleep but their heart health as well.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the signs of high blood pressure related to poor sleep?
+
Signs may include headaches, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating, often exacerbated by inadequate sleep.
How does diet impact sleep and blood pressure?
+
A balanced diet rich in nutrients supports better sleep and helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
What are some natural remedies to improve sleep quality?
+
Natural remedies include herbal teas, maintaining a bedtime routine, and practicing relaxation techniques.