Discover the profound connection between obstructive sleep apnea in children and behavioral difficulties. Learn how timely diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve their neurobehavioral functioning.
The Link Between Sleep Apnea and Behavioral Issues
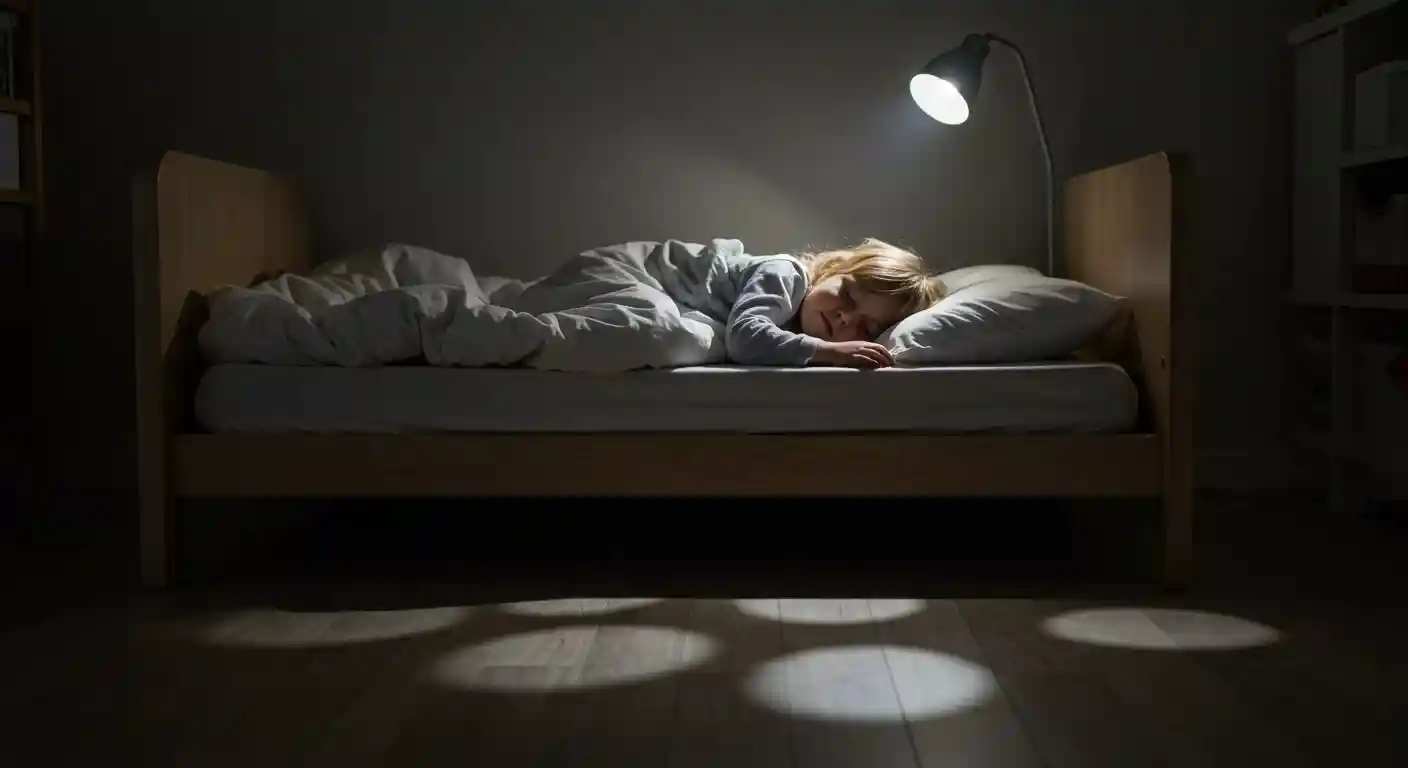
Children with sleep apnea are at a significantly higher risk of developing ADHD-like behavioral problems and experiencing difficulties with learning and adaptive skills. The study conducted over five years underscored the prevalence of SDB in children aged 6 to 11 and highlighted the impact of untreated sleep apnea on their neurobehavioral functioning. The findings revealed that children with persistent sleep apnea exhibited a considerably higher incidence of behavioral and learning issues compared to those without SDB.
Early Diagnosis and Timely Intervention
While some cases of OSA may improve with age, it is vital to diagnose and treat sleep apnea promptly in children. Treatment options often involve surgical interventions, such as the removal of tonsils and adenoids, or the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. Early identification and management of sleep apnea can lead to significant improvements in behavioral problems, attention span, and academic performance among affected children.
Understanding Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children
Obstructive sleep apnea affects approximately two percent of healthy children and is commonly characterized by enlarged tonsils and adenoids. Children with OSA often exhibit symptoms like loud snoring, pauses in breathing during sleep, and restless sleep patterns. Identifying these signs and symptoms early on can aid in the timely diagnosis of sleep apnea and prevent long-term implications on a child’s development.
Impact on Daily Functioning
Apart from behavioral and learning challenges, untreated sleep apnea can also impact a child’s daily functioning. Issues with hyperactivity, attention, social interactions, and self-care may arise due to disrupted sleep patterns and insufficient oxygen intake during sleep. Addressing these underlying sleep-related issues is crucial for enhancing a child’s overall well-being and academic performance.
Promoting Healthy Sleep Habits in Children
Encouraging healthy sleep habits and routines is vital in preventing and managing sleep apnea in children. Ensuring a conducive sleep environment, limiting screen time before bed, and establishing consistent bedtime routines can significantly improve sleep quality and reduce the risk of SDB. Parents and caregivers play a pivotal role in fostering healthy sleep practices that support children’s cognitive development and overall health.
Conclusion
The profound impact of obstructive sleep apnea on children’s behavior and learning underscores the critical need for early detection and intervention. By recognizing the signs of sleep apnea, promoting healthy sleep practices, and seeking timely medical assistance, parents and caregivers can support children in overcoming the challenges associated with SDB. Prioritizing children’s sleep health is key to fostering optimal neurobehavioral functioning and academic success.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I identify signs of sleep apnea in my child?
Signs of sleep apnea in children may include loud snoring, pauses in breathing during sleep, restless sleep patterns, and daytime fatigue. Consult a healthcare provider if you notice these symptoms to explore further evaluation and diagnosis.
What treatment options are available for children with sleep apnea?
Treatment for pediatric sleep apnea often involves surgical interventions, such as the removal of tonsils and adenoids, or the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. Collaborate with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable treatment approach for your child’s specific needs.
Sources
- National Sleep Foundation: https://www.sleepfoundation.org
- Mayo Clinic – Sleep Health: https://www.mayoclinic.org
- NIH – Neurological Disorders: https://www.ninds.nih.gov
- CDC – Sleep and Sleep Disorders: https://www.cdc.gov/sleep
- WebMD – Sleep Disorders: https://www.webmd.com/sleep-disorders
- Healthline – Sleep: https://www.healthline.com/health/sleep