Introduction
In our fast-paced society, where work and social obligations dominate our schedules, sleep often becomes a luxury rather than a necessity. Many of us sacrifice precious hours of slumber in favor of productivity or leisure, not fully understanding the toll this can take on our health. While missing a few nights of sleep here and there may not appear to have significant consequences, the dangers of long-term sleep deprivation are far more serious than most people realize.
Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Gain
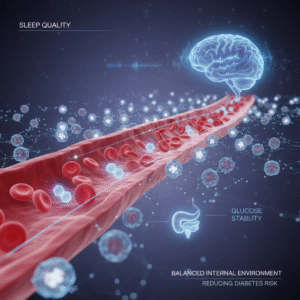
Moreover, chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to the development of obesity due to its impact on insulin sensitivity. When we do not get enough sleep, our bodies struggle to process insulin effectively, leading to higher blood sugar levels and increased fat storage. This phenomenon contributes not only to weight gain but also elevates the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, a condition that affects millions worldwide.
Mental Health Decline
A lack of sleep can impair cognitive functions, making it harder to concentrate, solve problems, and make decisions. This mental fatigue can contribute to an overwhelming sense of hopelessness, further exacerbating existing mental health conditions. Over time, untreated sleep deprivation may lead to more severe psychiatric issues, including anxiety disorders and major depressive disorders.
Looking for the best option related to Long-Term Sleep Deprivation Risks?
The Sleep Bridge recommends checking the latest deals and reviews before purchasing to ensure better sleep quality.
Cardiovascular Disease
Chronic sleep loss can lead to higher levels of cortisol, a hormone that, when elevated, contributes to high blood pressure and increased arterial stiffness. Furthermore, sleep deprivation is often accompanied by unhealthy lifestyle choices—such as poor diet and lack of exercise—that compound the risk of cardiovascular disease. Prioritizing sleep is, therefore, essential for maintaining a healthy heart and reducing the likelihood of developing serious heart-related conditions in the long run.
Impaired Immune Function
Over time, chronic sleep deprivation can lead to long-lasting impacts on immune health, increasing the risk of autoimmune disorders and chronic inflammation. Research suggests that people who fail to get sufficient sleep not only contract illnesses more frequently but may also experience a longer recovery time. Thus, ensuring adequate sleep is critical for maintaining a robust immune system and overall health resilience.
Cognitive Decline and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Furthermore, chronic sleep deprivation may accelerate cognitive declines, impacting memory, attention span, and decision-making abilities. In older adults, these cognitive deficits become even more concerning, as they may overly increase the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. Prioritizing sleep is not merely beneficial for immediate cognitive function; it is also a preventative measure for long-term brain health.
Conclusion
While the demands of daily life can make adequate sleep seem like a low priority, the long-term consequences of sleep deprivation are far too significant to ignore. From hormonal imbalances and mental health challenges to cardiovascular issues, impaired immune function, and cognitive decline, the risks are profound and multifaceted. Recognizing the importance of sleep and making conscious efforts to prioritize it can lead to improved overall health and set the stage for a more fulfilling life.
The dark side of sleep deprivation serves as a critical reminder: Sleep is not merely a luxury; it is an absolute necessity for our health and well-being. By making sleep a priority, we can not only enhance our quality of life but also mitigate the grim realities associated with long-term sleep deprivation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some signs that I may be sleep deprived?
+
Common signs of sleep deprivation include fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and increased appetite.
Can sleep deprivation affect my physical health?
+
Yes, chronic sleep deprivation can lead to serious health issues, including obesity, heart disease, and a weakened immune system.
How much sleep do adults need to function optimally?
+
Most adults require 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night for optimal health and functioning.